In my previous post I explained what is PKI and how it works. You can find it using http://www.rebeladmin.com/2018/05/how-pki-works/
Active Directory Certificate Service is the Microsoft solution for PKI, It is collection of role services and those can use to design the PKI for your organization. In this post we are going to look in to each of these role service and their responsibilities.
Certificate Authority (CA)
CA role service holders responsible for issue, store, manage and revoke certificates. PKI setup can have multiple CAs. There are mainly two types of CA which can identify in PKI.
Root CA
Root CA is the most trusted CA in PKI environment. Compromise of root CA will possibly compromise entire PKI. There for security of the root CA is critical and most organization only bring those online when they need to issue or renew a certificate. Root CA also capable of issue certificates to any object or services but considering security and hierarchy of the PKI it used to issue certificates only to Subordinate CAs.
Subordinate CA
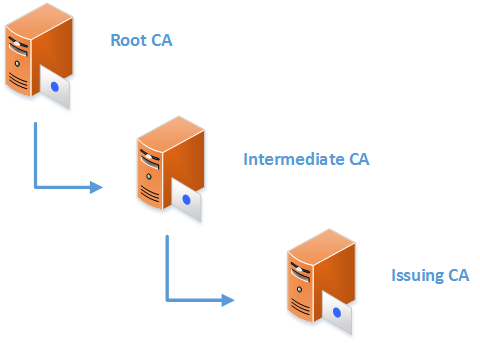
In PKI, Subordinate CAs are responsible for issues, store, manage and revoke certificates for objects or services. These publish certificate templates and users can create their certificate requests based on those templates. Once CA receives the request it will process it and issue the certificate. PKI can have multiple subordinate CAs. Each subordinate server should have its own certificate from the root CA. the validity period of these certificates is normally longer than ordinary certificates. It also need to renew its certificate from root CA when it reaches the end of validity period. Subordinate CA can have more subordinate CAs below it. in such situation, Subordinate CA also responsible for issuing certificates for its more subordinate CAs. These Subordinate CAs which have more Subordinate CAs called as Intermediate CA. These will not be responsible for issues certificates to users, devices or services. Then it will become more subordinate CA’s responsibilities. The more subordinate servers which issues certificates will call as Issuing CA.
Certificate Enrollment Web Service
Certificate enrolment web service allow users, computer or services to request certificate or renew certificate via web browser, even it is not domain-joined or temporally out of corporate network. If it is domain-joined and in corporate network, they can use auto enrollments or template based request process to retrieve certificate. This web service will remove the dependencies to use other enrollment mechanism.
Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service
This role service is works with certificate enrollment web service and allow user, computer or services to perform policy-based certificate enrollment. Similar to enrollment web services, the client computers can be non-domain joined computer or domain joined devices which is out of company network boundaries. When client request for policy information, enrollment policy web service query the AD DS using LDAP for the policy information and then deliver it to client via HTTPS. This information will be cashed and use for similar requests. Once user has the policy information then he/she can request certificate using certificate enrollment web service.
Certificate Authority Web Enrollment
This is similar to a web interface for Certificate Authority. Users, computers or services can request certificates using web interface. Using the interface users also can download the root certificates and intermediate certificates in order to validate the certificate. This also can use to request certificate revocation list (CRL). This list includes all the certificates which is expires or revoked with in its PKI. If any presented certificate match entry in the CRL, it will be automatically refused.
Network Device Enrollment Service
Network devices such as routers, switch and firewalls can have device certificates to verify authenticity of traffic pass through it. majority of these devices are not Domain-Joined and their operation system are also very unique and do no support typical windows computer functions. In order to request or retrieve certificates, it uses Simple certificate enrollment protocol (SCEP). It allows network devices to have x.509 version 3 certificates similar to other domain-joined devices. This is important as if devices going to use IPsec it must needs have x.509 version 3 certificate.
Online Responder
Online responder is responsible for producing information about certificate status. When I explain about CA web enrollment I explained about certificate revocation list (CRL). CRL includes the entire list of certificates which is expired and revoked with in the PKI. The list will keep growing based on the number of certificates it managed. Instead of using bulk data, online responder will response to individual requests from users to verify status of a particular certificate. This is more efficient than CRL method as requests is focused to find out status of one certificate in given time.
Certificate Authority Types
Based on the installation mode the CAs can be divide in to two types which is Standalone CA and Enterprise CA. The best way to explain capabilities of both types is to compare them.
|
Feature |
Standalone CA |
Enterprise CA |
|
AD DS Dependency |
Not Depend on AD DS, it can install on member server or stand-alone server in workgroup |
Only can install in Member server |
|
Operate Offline |
Can Stay Offline |
Cannot be Offline |
|
Customized Certificate Templates |
Do Not support, only support standard templates |
Supported |
|
Supported Enrollment Methods |
Manual or Web Enrollment |
Auto, Manual or Web Enrollment |
|
Certificate Approval Process |
Manual |
Manual or Automatic based on the Policy |
|
User input for the Certificate fields |
Manual |
Retrieved from AD DS |
|
Certificate Issuing and Managing using AD DS |
N/A |
Supported |
Standalone CA mostly use for as the root CA. in previous section I have explain how important is root CA security is. In Standalone CA it support to keep the server offline and bring it online when it need to issue certificate or renew certificate. Since root CA are only used to issue certificates to subordinate CA. so the manual processing and approval are manageable as it may only have to do in every few years’ time. This type also valid for public CAs. Issuing CA are involving with day to day certificate issuing, managing, storing, renewing and revoking process. Depending on the infrastructure size it can be hundreds or thousands who use these issuing CAs. If the request and approval process is manual it may take much manpower to maintain it. there for in corporate networks it always recommended to use enterprise CA type. Enterprise CAs allows engineers to create certificate templates with specific requirements and publish these via AD DS. End users can request the certificates based on these templates. Enterprise CAs are only can install on Windows server Enterprise or Data Center version only.
This marks the end of this blog post. In next post we are going to look in to deployment models of AD CS. If you have any questions feel free to contact me on rebeladm@live.com also follow me on twitter @rebeladm to get updates about new blog posts.



Thanks you so much sir, I would like to request to publish about Network Policy Sever with ADCS.